This document lists some useful examples about using MIDP.
1. Preparation
1.1. Package installation
The used python version is 3.7. One can install this package locally by cloning the repo and running
python setup.py install --user
or install it by pip
pip install git+https://github.com/YuanYuYuan/MIDP
1.2. Download sample dataset
In the following examples, we use the PDDCA dataset as the sample dataset, and name it as data.
The structure of PDDCA dataset is like the following and in NRRD data format(.nrrd).
data
├── 0522c0002
│ ├── img.nrrd
│ └── structures
│ ├── Brainstem.nrrd
│ ├── Chiasm.nrrd
│ ├── Mandible.nrrd
│ ├── OpticNerve_L.nrrd
│ ├── OpticNerve_R.nrrd
│ ├── Parotid_L.nrrd
│ ├── Parotid_R.nrrd
│ ├── Submandibular_L.nrrd
│ └── Submandibular_R.nrrd| In here we change the default "BrainStem" to "Brainstem". |
2. Tools
2.1. Data conversion
2.1.1. Resample the NRRD into consistent spacing
In consideration of fast model training under some consistent spacing, we’d better
resample the dataset and store it as a new fixed data.
Run the following command
to convert the dataset data into new dataset in spacing 1, and store them at the
directory resampeld_data.
./resample_nrrd_dataset.py --data data --spacing 1 --output-dir resampled_data
Although this program runs with multi processes, it might still take several minutes to finish it.
2.1.2. NRRD → NIfTI
The following one demos how to transfer the NRRD dataset to NIfTI dataset
./nrrd2nifti.py --config configs/nrrd2nifti.yaml
with a sample configuration configs/nrrd2nifti.yaml.
# Input directory containing NRRD data
data_dir: ./data
# Output directory storing NIfTI data
output_dir: ./nifti
# Unit: mm
spacing: 1
# TODO: correct ROIs to classes
# Map each structure to specified value
# For PDDCA dataset, there're
# Mandible : 1
# Brainstem : 2
# Parotid_L : 3
# Parotid_R : 4
# Submandibular_L : 5
# Submandibular_R : 6
# OpticNerve_L : 7
# OpticNerve_R : 8
# Chiasm : 9
# But note that some cases in PDDCA dataset may not contain all structures.
roi_map:
Brainstem : 1
Parotid_L : 2
Parotid_R : 3After converted, the output in NIfTI format should be located at the output_dir (nifti in this example).
2.1.3. NIfTI → NRRD
When doing backward conversion from NIfTI to NRRD,
it requires the information of the original dataset,
so you should specify the source data directory(data in this example).
The following one demo how to use the program to convert the label from NIfTI to NRRD.
./nifti2nrrd.py --nrrd-dir data --nifti-dir nifti/labels --output-dir restored
2.2. For training
2.2.1. Generate data list for training
-
Generate data list by parsing loader.
./generate_data_list.py \ --loader-config configs/parsing_loader.yaml \ --output data_list.yaml[Example]
data_list.yamlamount: test: 0 total: 48 train: 33 valid: 15 list: test: [] train: - 0522c0001 - 0522c0002 - 0522c0009 - 0522c0013 - 0522c0014 - 0522c0017 - 0522c0070 - 0522c0077 - 0522c0079 - 0522c0147 - 0522c0161 - 0522c0195 - 0522c0248 - 0522c0251 - 0522c0253 - 0522c0328 - 0522c0329 - 0522c0330 - 0522c0427 - 0522c0433 - 0522c0455 - 0522c0479 - 0522c0576 - 0522c0598 - 0522c0659 - 0522c0661 - 0522c0667 - 0522c0669 - 0522c0708 - 0522c0746 - 0522c0788 - 0522c0806 - 0522c0878 valid: - 0522c0003 - 0522c0057 - 0522c0081 - 0522c0125 - 0522c0132 - 0522c0149 - 0522c0159 - 0522c0190 - 0522c0226 - 0522c0441 - 0522c0457 - 0522c0555 - 0522c0727 - 0522c0845 - 0522c0857 loader: name: ParsingLoader parser_config: - ROIs: - Brainstem - Parotid_L - Parotid_R data_dir: data name: PDDCAParser preprocess_image: false -
Generate data list by nifti loader.
./generate_data_list.py \ --loader-config configs/nifti_loader.yaml \ --output data_list.yaml[Example]
data_list.yamlamount: test: 0 total: 2 train: 1 valid: 1 list: test: [] train: - 0522c0598 valid: - 0522c0576 loader: data_dir: nifti name: NIfTILoader -
Generate data list by NRRD loader.
./generate_data_list.py \ --loader-config configs/nrrd_loader.yaml \ --output data_list.yaml[Example]
data_list.yamlamount: test: 0 total: 48 train: 33 valid: 15 list: test: [] train: - 0522c0002 - 0522c0013 - 0522c0014 - 0522c0057 - 0522c0081 - 0522c0125 - 0522c0132 - 0522c0147 - 0522c0149 - 0522c0159 - 0522c0161 - 0522c0190 - 0522c0195 - 0522c0248 - 0522c0251 - 0522c0329 - 0522c0330 - 0522c0433 - 0522c0441 - 0522c0457 - 0522c0479 - 0522c0555 - 0522c0576 - 0522c0598 - 0522c0661 - 0522c0667 - 0522c0669 - 0522c0708 - 0522c0727 - 0522c0788 - 0522c0806 - 0522c0845 - 0522c0878 valid: - 0522c0001 - 0522c0003 - 0522c0009 - 0522c0017 - 0522c0070 - 0522c0077 - 0522c0079 - 0522c0226 - 0522c0253 - 0522c0328 - 0522c0427 - 0522c0455 - 0522c0659 - 0522c0746 - 0522c0857 loader: data_dir: data name: NRRDLoader roi_map: Brainstem: 1 Parotid_L: 2 Parotid_R: 3 -
Generate data list by NRRD loader and toggle resampling.
./generate_data_list.py \ --loader-config configs/nrrd_loader_resample.yaml \ --output data_list.yaml[Example]
data_list.yamlamount: test: 0 total: 48 train: 33 valid: 15 list: test: [] train: - 0522c0001 - 0522c0013 - 0522c0014 - 0522c0017 - 0522c0057 - 0522c0070 - 0522c0077 - 0522c0079 - 0522c0081 - 0522c0125 - 0522c0132 - 0522c0147 - 0522c0149 - 0522c0159 - 0522c0195 - 0522c0226 - 0522c0248 - 0522c0251 - 0522c0330 - 0522c0427 - 0522c0433 - 0522c0441 - 0522c0455 - 0522c0457 - 0522c0479 - 0522c0555 - 0522c0576 - 0522c0598 - 0522c0667 - 0522c0727 - 0522c0788 - 0522c0806 - 0522c0857 valid: - 0522c0002 - 0522c0003 - 0522c0009 - 0522c0161 - 0522c0190 - 0522c0253 - 0522c0328 - 0522c0329 - 0522c0659 - 0522c0661 - 0522c0669 - 0522c0708 - 0522c0746 - 0522c0845 - 0522c0878 loader: data_dir: data name: NRRDLoader resample: true roi_map: Brainstem: 1 Parotid_L: 2 Parotid_R: 3 spacing: 1 test: false -
Generate data list by NRRD loader and split it into training/validation/testing 3 parts with a ratio 6:2:2.
./generate_data_list.py \ --loader-config configs/nrrd_loader.yaml \ --output train_valid_test_list.yaml \ --split-ratio 0.6 0.2
[Example]
train_valid_test_list.yamlamount: test: 11 total: 48 train: 28 valid: 9 list: test: - 0522c0003 - 0522c0070 - 0522c0132 - 0522c0147 - 0522c0161 - 0522c0427 - 0522c0433 - 0522c0441 - 0522c0661 - 0522c0845 - 0522c0878 train: - 0522c0001 - 0522c0002 - 0522c0009 - 0522c0013 - 0522c0014 - 0522c0017 - 0522c0077 - 0522c0079 - 0522c0081 - 0522c0149 - 0522c0190 - 0522c0195 - 0522c0248 - 0522c0253 - 0522c0328 - 0522c0329 - 0522c0330 - 0522c0455 - 0522c0457 - 0522c0479 - 0522c0555 - 0522c0659 - 0522c0667 - 0522c0669 - 0522c0708 - 0522c0727 - 0522c0746 - 0522c0857 valid: - 0522c0057 - 0522c0125 - 0522c0159 - 0522c0226 - 0522c0251 - 0522c0576 - 0522c0598 - 0522c0788 - 0522c0806 loader: data_dir: data name: NRRDLoader roi_map: Brainstem: 1 Parotid_L: 2 Parotid_R: 3
2.2.2. Training pipeline design
A sample structure has been written in sample_train.py with a example config configs/training.yaml.
./sample_train.py --config configs/training.yaml
Note that the config/training.yaml assumes a data list file at data_list.yaml.
2.3. Find bounding boxes
You can modify the data loader to specify which structures to enclose, and choose a proper padding to obtain a larger box.
./find_box.py \
--config configs/nrrd_loader_eyes.yaml \
--output bbox.json \
--padding 20
After finished, you will obtain a bbox.json file, which can be used
in the 2nd stage segmentation.
3. Testing
3.1. Data loader
Directly use parser to load data
./sample_loader.py --loader-config configs/parsing_loader.yaml
or use NIfTI data loader(but required conversion beforehand).
./sample_loader.py --loader-config configs/nifti_loader.yaml
This program will launch a viewer of the data, you can scroll the mouse wheel to change the slice.
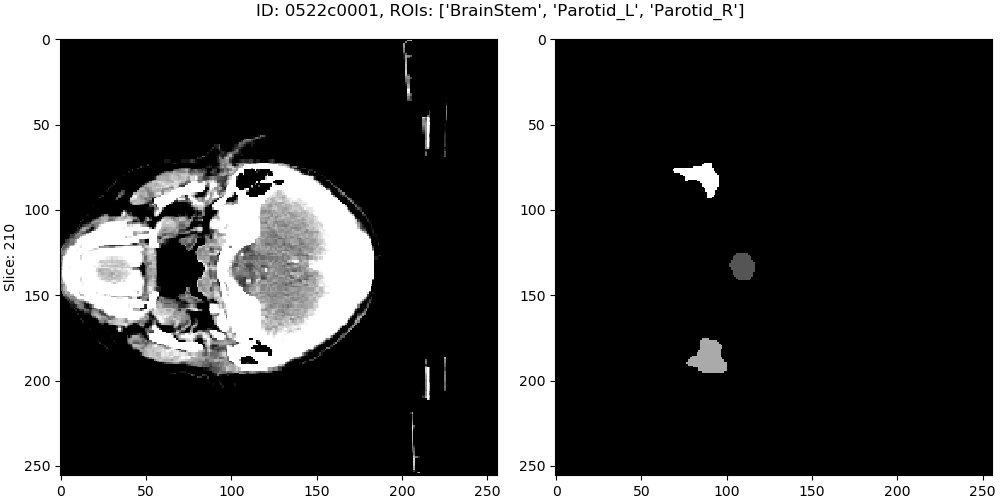
3.2. Data generator
Directly use parser to load data
./sample_generator.py \
--loader-config configs/parsing_loader.yaml \
--generator-config configs/generator.yaml \
--output-dir outputs
or use NIfTI data loader(but required conversion beforehand).
./sample_generator.py \
--loader-config configs/nifti_loader.yaml \
--generator-config configs/generator.yaml \
--output-dir outputs
with a example generator config configs/generator.yaml.
BlockSampler : # sample a 3D block from each data(3D image)
shuffle : True # shuffle the data list
block_shape : [128, 128, 30] # the shape of observing area, i.e shape of image
out_shape : [96, 96, 20] # the valid shape of the block, i.e. shape of label
n_samples : 32 # number of samples of each data
ratios : [0, 1, 2, 2] # sampling probability of each class, note the lenght should be the same with the number of classes
n_workers : 2 # number of multi-thread workers
verbose : False # toggle the debug info of this generator
Augmentor : # do preprocessing and data augmentation
zoom_range : [0.8, 1.2] # zoom the image/label with some scale in range, note that it only apply on x-y plane
transpose : True # transpose the image/label on x-y plane with a fixed probability 0.5
flip : True # flip the image/only on x-y plane with a fixed probability 0.5
noise : True # add a Gaussian noise with mean 0 and sigam 0.05 on the image
window_width : [90, 110] # adjust the contrast with the given window width(or a range), default : 100
window_level : [40, 60] # adjust the contrast with the given window level(or a range), default : 50
n_workers : 2 # number of multi-thread workers
verbose : False # toggle the debug info of this generator
BatchGenerator : # pack the processed data into batches
batch_size : 32 # batch size
n_workers : 2 # number of multi-thread workers
verbose : False # toggle the debug info of this generatorThe output files are stored in 3D NIfTI (nii.gz) in the outputs folder.
One may view these images by ITK-SNAP.
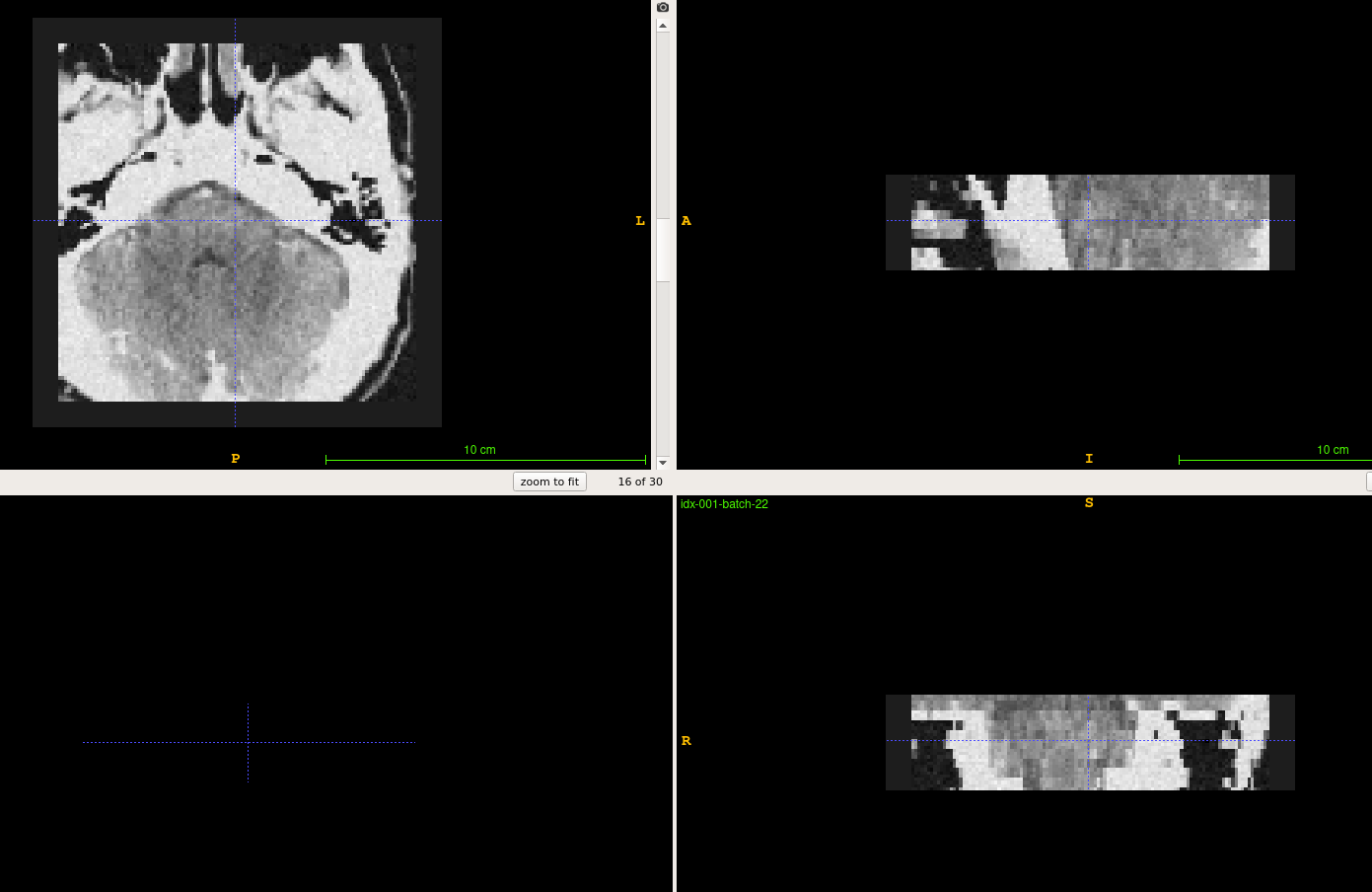
3.3. Check the data generator of bs-ptd-v2
Run the following command to check the data pipeline is fine.
./sample_generator.py \
--loader-config configs/nrrd_loader.yaml \
--generator-config configs/bs-ptd-v2-generator.yaml
This nrrd_loader.yaml doesn’t toggle resampling.
If you didn’t run conversion beforehand, please
use nrrd_loader_resample.yaml instead.
|
You can find tune the generator config to run on this test, that is modify
BlockGenerator :
block_shape : [96, 96, 96]
stride : 48
crop_shape : [256, 256, -1]
n_workers : 4
ordered : True
queue_size : 4 # unit: whole 3D volume from each scan (1)
verbose : False
Augmentor :
window_width : 100
window_level : 50
n_workers : 1
queue_size : 4 # unit: small blocks extracted from 3D volume (1)
verbose : False
BatchGenerator :
batch_size : 24 (2)
n_workers : 1
queue_size : 4 # unit: batch data of size=batch_size (1)
verbose : False| 1 | Find a proper queue_size of max size of the data queue according to your CPU memory.Note that the default size is 4. And setting it to 0 means unlimited queue_size. |
| 2 | Find a proper batch_size according to your GPU memory. |
Large batch_size may not help the speed, it also depends on the utilization of GPUs.
If you have found that the utilization of GPUs(can be monitored by running nvtop or watch -n1 nvidia-smi) has been full,
then increasing the batch size won’t speedup the process.
|